Lecture 12, part 2 of 3
| PLNT4610/PLNT7690
Bioinformatics Lecture 12, part 2 of 3 |
RNA sequencing is not
perfect. At the analytical level, it has a number of potential
problems that must be corrected for in the analytical pipeline.
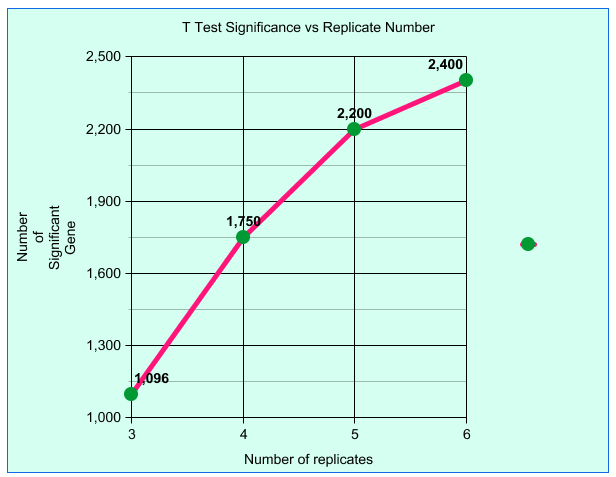
| Plotting T test results for number of
significant results vs biological replicates creates a
flattening curve indicating diminishing returns beyond 6
replicates. Fold test line (not shown) is flat indicating. In microarray experiments, a dataset of 6 biological replicates was sampled to create test datasets containing all possible permutations of 3, 4, 5 or 6 replicates. Results for 3, 4 and 5 replicates are an average, while results for 6 replicates means that all 6 replicates were used. Although these results used microarray data, the same statistical principles apply to RNA-seq data. Björklund, Natalie (2012) University of Manitoba. |
 |
BIOLOGICAL REPLICATES ARE THE SINGLE MOST EFFECTIVE WAY TO GET GOOD GENE EXPRESSION RESULTS!In the next section we will see that there is an almost endless list of ways to massage the data. The most heroic analytical methods are no substitute for the simple step of doing several biological replicates.
Estimated number of replicated needed for a sample dataset
Power is the fraction of true positives detected. FDR is the false discovery rate ie. false positives. The numbers either side of the right slash indicate sample-size (ie. biological replicates) estimates made using the sample-size estimation methods described in Ref. [8] and Ref. [10], respectively. Simon, S. Myths & Truths About
Microarray Expression Profiling Conclusions
|
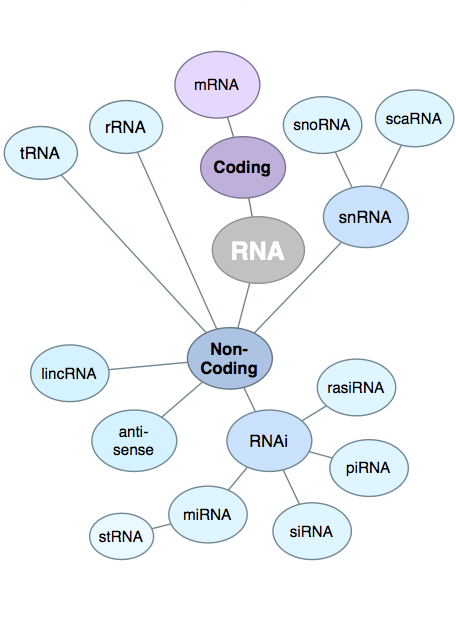
| While
in general the quality of the RNA is important to the
success of RNA-seq experiments, the parameter that has the
most effect is the degree to which the sample has been
enriched for mRNA, by eliminating other RNAs. Especially
in Eukaryotic RNA populations, mRNA usually makes up only
a few percent of the total, which is predominantly rRNA.
If no enrichment procedure was done, the depth of coverage
of protein coding genes would be greatly compromised,
because the vast majority of reads would be rRNA. Although most RNA-seq library preparation protocols have a step for enriching for mRNAs, there will always be contamination from other RNAs. For this reason, it is important that there be a step in the RNA pipeline to eliminate reads that can be identified as other forms of RNA, such as rRNA or tRNA. Image from http://finchtalk.geospiza.com/2009/05/small-rnas-get-smaller.html |
 |
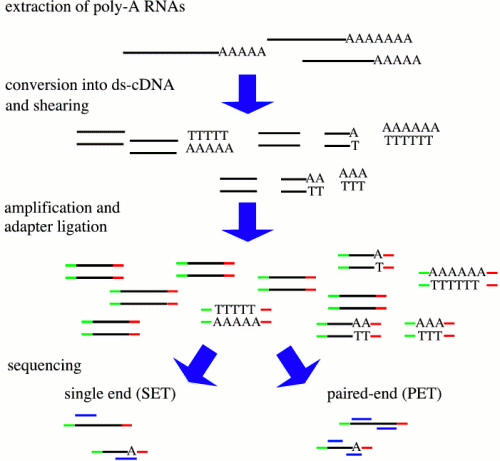
| There
are many protocols for RNA sequencing, including Illumina
GA/HiSeq, and Roche 454. Although these differ, the
RNA-seq can be described generally as shown at right. from http://cmb.molgen.mpg.de/2ndGenerationSequencing/Solas/RNA-seq.html In some protocols, RNA is sheared, followed by random hexamer priming. In other protocols, the entire mRNA transcript is used as a template for cDNA synthesis, and the cDNA is fragmented. Adapters for PCR are ligated onto ds-cDNA, followed by PCR amplification. Sequencing reactions are either done from a single end, or for both ends (paired-end). |
 |
 Unless otherwise cited or
referenced, all content on this page is licensed under
the Creative Commons License Attribution
Share-Alike 2.5 Canada Unless otherwise cited or
referenced, all content on this page is licensed under
the Creative Commons License Attribution
Share-Alike 2.5 Canada |
| PLNT4610/PLNT7690
Bioinformatics Lecture 12, part 2 of 3 |