3. Turning web data into objects
a. XML
- Extended Markup Language
Languages such as Java,
C++, Perl and Python, are designed to allow networked objects to
communicate with one another. The nature of the data must be
hard-coded into the programs, or into the database
definition.
Another approach to
data interchange between objects is XML. XML is a protocol
for defining datafile formats. It is not a file format per se.
Rather, XML standardizes how data files are defined.
- Data Definition
- DTD - Document
Type Definition
Remember, XML is not so much a language as a standard for
describing a data object. For each new type of data object
it is necessary to write a DTD to specify how the object is
structured. The names of all elements and their components
are defined.
- Schema
The DTD is limited to the description of data elements with
simple text fields. While this model is adequate for most
text documents, the definition of more complex data elements
requires a schema. A schema (written in XML) describes
relationships between data objects, as in a database.
Numeric elements can also be described, unlike DTDs, in
which numbers are represented as text. Constraints can be
placed on data elements (eg. nucleotide can take the value
A,G,C,T,U or N; the number of strands may have the value 1
or 2). The specification of constraints in the schema makes
it possible to automatically validate an XML file.
- XML - an instance of data following the
specifications of the DTD or schema
Usually, an
application will check each XML file to make sure it conforms
to the DTD. If valid, the XML file is read, and the
corresponding data objects are created.
EXAMPLE: The pea
disease resistance response gene DRR206 is found in UniProtKB
in entry P13240.
- XSL - XML stylesheet language
One of the most important uses for XML is as an alternative to
HTML. HTML is limited to displaying text in a fairly simple
fashion. XML allows the creation of rich data types. However,
XML files, unlike HTML, don't specify how data are to be
displayed in a browser. Therefore, XML stylesheets can be
written for each type of XML file, providing a consistent
structure to XML document presentation. Most of the major web
browsers (Safari, Edge, Mozilla, Firefox) provide at least
some XML support.
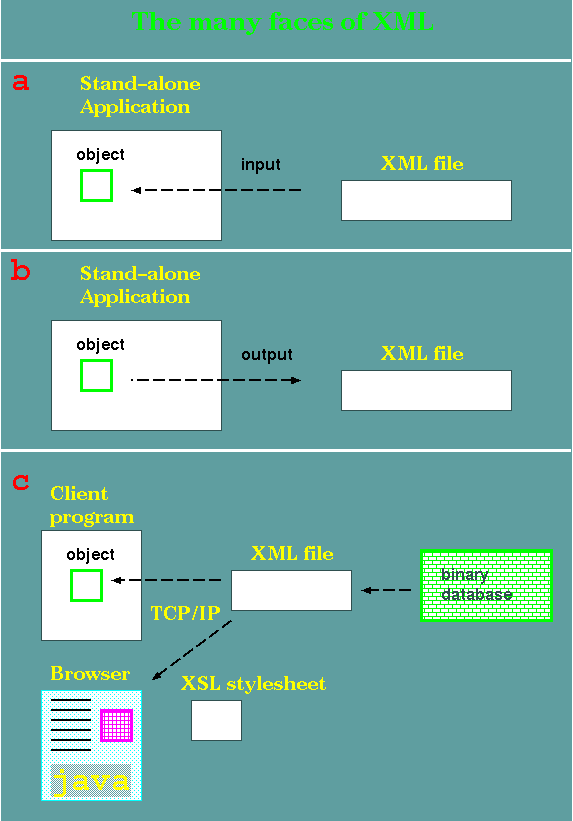
a -In this
example, an application has been programmed to read a specific
type of XML file. An object is created within the application
based on the specifications in the XML file.
b - Conversely to a, an
object in the application is translated to an XML
representation, and written to a file.
c - This is a complex
example. Data from a binary database is written to an XML file.
At top, an client program, specialized for this particular XML
data type, reads the XML and creates an object.
If a stylesheet exists
for this XML data type, a browser can import the same XML file
and render it as a Web page. In this case, a complex page,
consisting of text, graphics, and a Java applet, is rendered.
Most of the widely-used languages (Java, C++, Python, Perl) have
extensive libraries for reading, writing and manipulating XML
objects.
b.
Ontologies - relationships beteween data objects
Open Biomedical Ontologies [http://obo.sourceforge.net]
Gene Ontology [http://www.geneontology.org/]
Controlled vocabulary - A controlled
vocabulary is an established list of standardized terminology for
use in indexing and retrieval of information. In a controlled
vocabulary, every object has an agreed-upon name, for which there
may be many synonyms. Regardless of the synonym used, it is
possible to find the name used by the controlled vocabulary.
Ontology - "... an
explicit specification of some topic. For our purposes, it is a
formal and declarative representation which includes the
vocabulary (or names) for referring to the terms in that subject
area and the logical statements that describe what the terms are,
how they are related to each other, and how they can or cannot be
related to each other. Ontologies therefore provide a vocabulary
for representing and communicating knowledge about some topic and
a set of relationships that hold among the terms in that
vocabulary (From the Stanford Knowledge Systems Lab)."
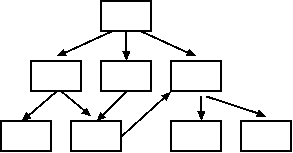 Ontologies are designed as Directed Acyclic Graphs
(DAG). DAGs have the following properties:
Ontologies are designed as Directed Acyclic Graphs
(DAG). DAGs have the following properties:
- Hierarchical tree-like structure
- Vertices (branches) are unidirectional, from less specific to
more specific
- Any node may have multiple parents
- Cross-branching may occur between objects at different levels
- Any path from a node must not lead back to that node (ie.
acyclic)
In an
ontology, relationships
between nodes are
defined. Usually, only a small number of relationships need to be
defined. This will be illustrated using Gene Ontology as an
example.
Gene Ontology
The goal of Gene Ontology is to create a formal description of the
relationships among genes and proteins and their cellular roles.
The current GO defines three high-level categories: Biological
Process, Molecular Function and Cell Component.
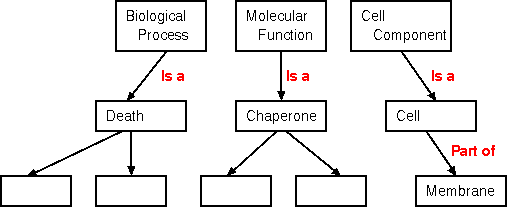
As illustrated above, relationships between objects are also
defined.
Example:
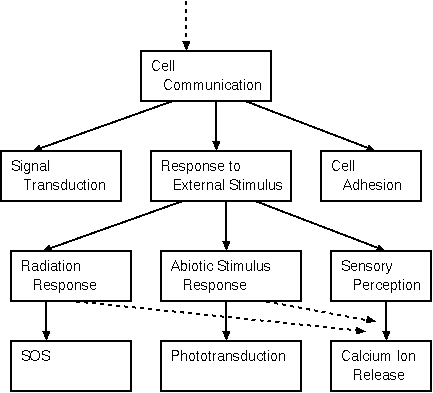
The entire GO tree can be viewed or searched at http://geneontology.org
Gene ontologies are often cited
in sequence and genome annotation.
Example:
Annotation extracted from GenBank protein entry EFN87342:
LOCUS
EFN87342
566
aa
linear INV 13-MAR-2015
DEFINITION Laccase, partial [Harpegnathos
saltator].
ACCESSION EFN87342
VERSION EFN87342.1
. . .
. . .
CDS
1..566
/locus_tag="EAI_07108"
/coded_by="join(GL446704.1:<19400..19480,
GL446704.1:19901..20058,GL446704.1:20718..20985,
GL446704.1:21349..21553,GL446704.1:21739..21929,
GL446704.1:22005..22212,GL446704.1:22356..22592,
GL446704.1:23026..23259,GL446704.1:27335..27453)"
/note="GO_function: GO:0005507 -
copper ion binding
[Evidence IEA];
GO_function: GO:0016491 -
oxidoreductase activity
[Evidence IEA];
GO_process: GO:0055114 - oxidation
reduction [Evidence
IEA]"
/db_xref="InterPro:IPR001117"
/db_xref="InterPro:IPR011706"
/db_xref="InterPro:IPR011707"
/db_xref="UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot:O59896"
There are three GO references: to copper ion binding,
oxidoreductase activity and oxidation reduction. All three are
probably closely related.
 Ontologies are designed as Directed Acyclic Graphs
(DAG). DAGs have the following properties:
Ontologies are designed as Directed Acyclic Graphs
(DAG). DAGs have the following properties:

 Unless otherwise cited or
referenced, all content on this page is licensed under
the Creative Commons License Attribution
Share-Alike 2.5 Canada
Unless otherwise cited or
referenced, all content on this page is licensed under
the Creative Commons License Attribution
Share-Alike 2.5 Canada