Binhua Liang
Assignment 4 --- PHYLOGENY
March 10, 2007
The problem
Six gamma-globin genes (four human and two chimp) are used for
pylogenetic analysis. The question is: is it valid to construct a
pylogenetic tree as a single unit, or do different parts of gene have
distinct evolutionary histories?
The approach to anwser....
(1) At first, print out
the alignments using "Alignment--->Reform? The alignment for working with...
(2) Construct a tree of the
entire alignment (Maximum Parsomony with bootstrapping): Outfile; Treefile
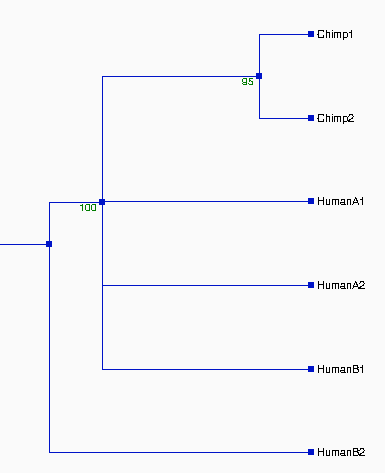
|
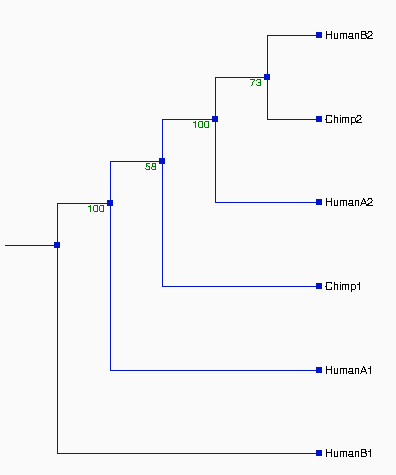
Figure 1. Pylogenetic Tree Produced From The
Entire Alignment
The resulted
tree on the left looks very good, which is
supported by high value of
bootstrapping (>92%).
The gamma globin genes are
reported to be subject
to gene
convertion--"noreciprocal transfer of genetic
information", which often occurs in a part
of gene. Thus,
some parts of gamma genes may have seperate
evolu-
tionary histories from other
region. The next step is to
investigate if different parts of the
sequence give differ-
ent trees (different
evolutionary histories).
|
|
|
(3) Decide a strategy to
define the parts of sequences which have different evolutionary
histories and build sub-tree based on the selected block of sequences.
In the paper, "Chimpanzee fetal Gr and Ar
Globin Gene Nucleotide Sequences Provide Further Evidence of Gene
Converstions in Hominine Evolution; Jerry L. Slightom, et.., Mol.Biol.Evol.2(5):370-398. 1985",
author postulates a possible conversions in a region of a sequence on
two conditions (1) Three or more substtutions and/or insertion/deletion
events are required in its descent from its immediate ancestor (2) at
least three fewer events would be necessary if the region had instead
descended from the homologous region of a paralogous gene in the same
taxon.
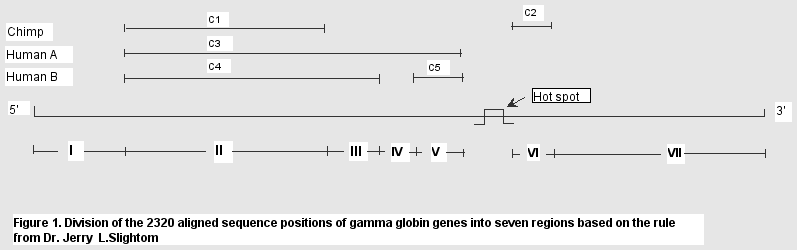
We use this criteria to predict the boudaries
of conversions of gamma globin gene sequences based on The Alignment. We predicted the following
boundaries of converstions of chmip, human A, and human B (gamma
globin genes):
---chimp: 324-1012, 1013-1183, 1732-1839
---humanA: 324-1698
---humanB: 324-1176, 1441-1681
According to the above predicted boundaries of
conversions, we divide the whole alignments (2320 bps) into 7
regions, see Figure 1 below:
(4) Building trees based on
the above defined regions of sequences, evaluating and comparing
the
resulted trees through bootstrapping
We built the individual trees based on
the above block of defined sequences using "Maximun Parsomony"
(DNAPARS). We set "Jumble the sequence order: Yes" and
"Resampling: Bootscrap = 100". Output files include: outfile
and outtree. We also captured tree images! The all results
are as following:
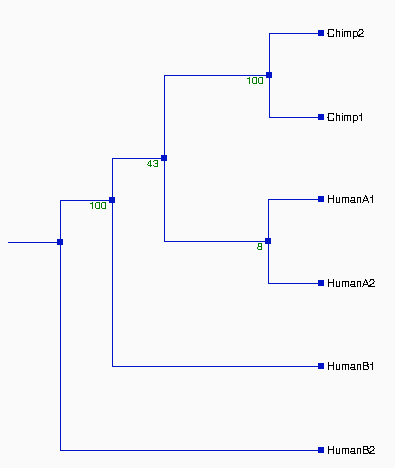
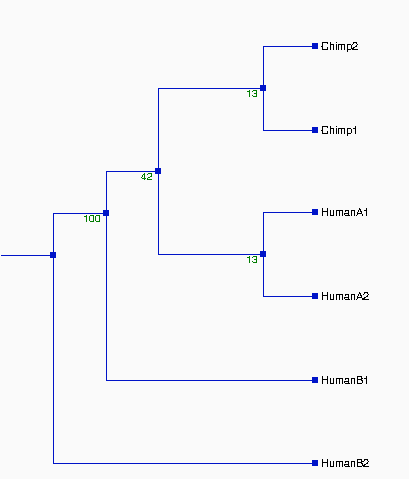
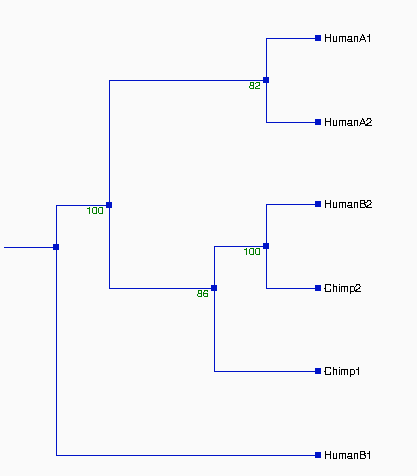
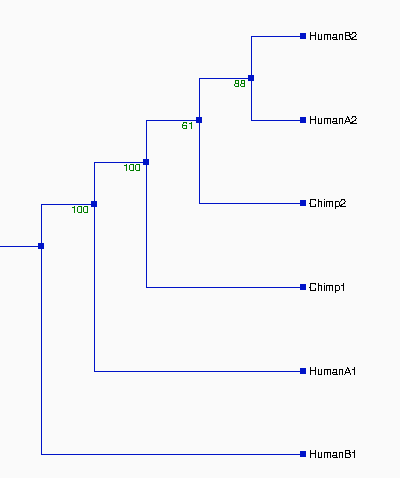
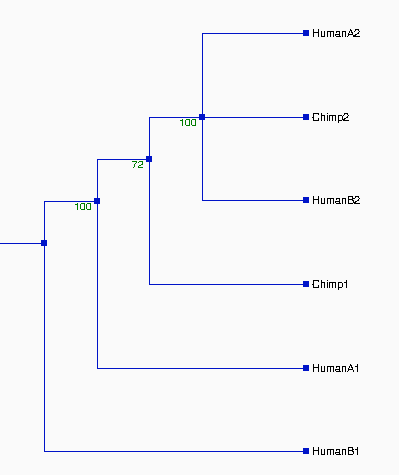
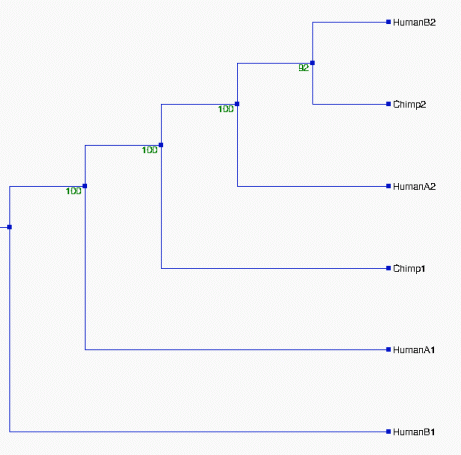
From the above tree topologies, we can see most of them are
different from one built from the whole alignment, except "Tree I".
(See figure 2). And the most of resulted trees are supported by
bootstrapping...
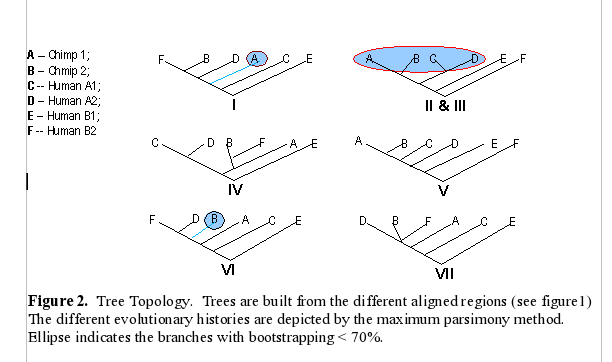
Except some branches, especially in Tree II & III with the
values of bootstrapping <50% (ellipse area, thus Tree II & III
not reliable), the most of resulted trees in Figure 2 are very
reliable, which are strongly supported by bootstrapping (>70%).
Although some branches in Tree I and VI, see figure 2, are not very
consistently replicated, their values of bootstrapping are 58% and
60%--- indicating that branches are clustered as above which are more
likely true in about 60% of trees and shoud not effect the
whole topologies of trees. Thus, the topologies of Tree I, IV, V, VI,
and VII should be reliable. Comparing the topologies of Tree I, IV, V,
VI, and VII with each other, we found that they are all different.
Because each mentioned tree is built from one region of gamma
globin gene, which gives a consistant tree across all bootstrapped
replicates, it probably has evolved as a coherent unit over time. The
above result suggests these regiones
defined from above to build different trees (I, IV,V,VI, and VII) may
represent different evolutionary histories.
Therefore, the gamma globin genes don't evolve as a single unit!
Conlusion
(1) All of parts of alignment of gamma globin gene don't share the
same tree since up to 5 regions show different trees.
(2) The whole alignment of gamma globin sequences can be broken up to
at least 5 distinct regions, which have separate evolutionary histories
from other regions. These 5 regions are defined as following (positions
below are based on The Alignment):
a. 1--324
b. 1277--1441
c. 1442--1681
d. 1732--1839
e. 1840--2320
In the region 325--1183, we should be more
cautious and take more analysis... ...
(3) The tree built from the entire alignment of gamma globin gene is
definitely not valid since up to 5 regions have evolved as a
coherent unit over time.
Return to My_Web_Site