
The following exercises are designed to help you understand the cell as a functional unit.
Diffusion (Canadian Campbell 2nd ed - Concept 7.3)
Molecules are in a constant state of motion. If, for example, NaCl is dissolved in water so that the NaCl molecules have a completely even and random distribution throughout the water, then there will be no net movement of NaCl in any direction. If however, the NaCl concentration is initially higher in one part of the water than another, diffusion will occur so that there is a net movement of NaCl from the area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration.
-What factors would influence the rate of diffusion?
-Where in an organism do you think diffusion would be an important process?
-What type of substances would enter and leave cells by simple diffusion?
Osmosis (Canadian Campbell 2nd ed - Concept 7.3)
The membrane of the cell or of various subcellular organelles (chloroplasts, mitochondria) serves as a regulatory structure by controlling the entry or exit of substances into and out of the cell. The membrane may be permeable, impermeable or partially permeable to a given substance. In general, membranes are freely permeable to water molecules. In cells, water movement through the cell membrane is determined by the process of osmosis.
During lab 3, three lengths of dialysis tubing were filled with a 2.0 M sucrose solution. A knot was then tied in the other end so that as much air as possible is excluded. The tubes were then rinsed in distilled water. The tubes were weighed and one tube each was placed in the following solutions.
At 15 minute intervals the sacs were removed weighed
View the results of the exercise
Which solution is:
View the correct answers of the exercise
Consider the following questions:
Plant Cells and Osmosis
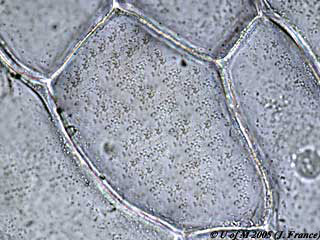
Recall the slide you made of the onion during lab 1 (click to view). Note the position and shape of the cell wall, cytoplasm and vacuole. Now view an onion section which has had a 10% NaCl solution added (click to view).
- What is the positional relationship of the cell wall to the protoplast?
You will find that the cytoplasm has shrunk away from the cell wall. The cell is said to be plasmolyzed.
This refers to the ability of substances to move into or out of the cell by crossing the plasma membrane. Some substances cross the membrane very easily and the membrane is said to be very permeable to these substances; others move across with difficulty, while others are excluded completely. In the latter case the cell membrane is impermeable to these substances.
During lab 3 you placed cut sections of beets in three solutions;

Answer the following questions about the exercise
One feature you have noticed in plant cells which is absent from animal cells
is a cell wall. This wall protects the protoplast and the membrane - plasmalemma.
![]() Return
to Biology Home
Return
to Biology Home ![]() Back
to Lab Index
Back
to Lab Index ![]() University
of Manitoba Home
University
of Manitoba Home