BIRCH
Workflow example: Use BLASTP
to search for sequences related to a query protein, within a specific
taxonomic group
The pea defense gene DRR206 confers strong resistance to fungal
pathogens when transformed into Brassica
napus. Although no Brassica
homologue of this gene has been found by hybridization, we would like
to see if a homologous sequence can be found in species closely-related
to B. napus. Since protein
searches are more sensitive than DNA
searches, we need to get the amino acid sequence from the genomic
sequence. This involves one step to extract the protein coding sequence
(CDS), and another to translate the CDS into protein.
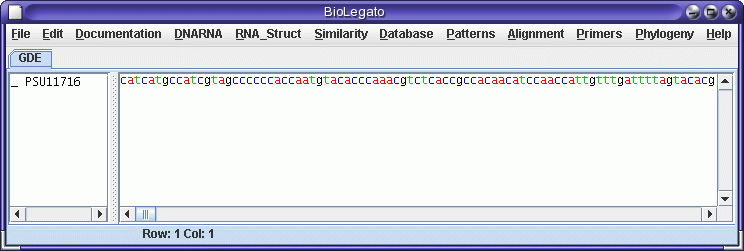
The first step is to read in GenBank file for the genomic sequence.
Save the file PSU1716l.gen in your
current working directory. In bldna, choose File --> Open,
and read in the file.
Next, we need to extract the protein coding sequence from the genomic
sequence. In GenBank files, coding sequences are annotated as CDS
features. Select the sequence and choose Database -->
FEATURES - Extract by feature keys:
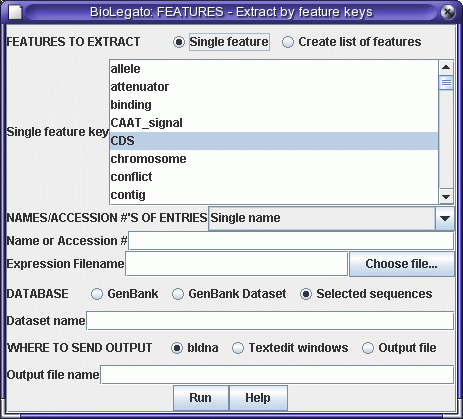
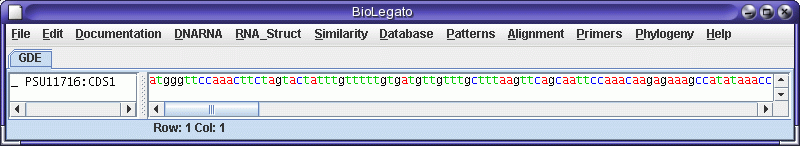
Set the feature key to CDS, Database to "Selected sequences", and send
output to bldna. A new bldna window pops up with the coding sequence
which
was extracted from the larger genomic sequence.
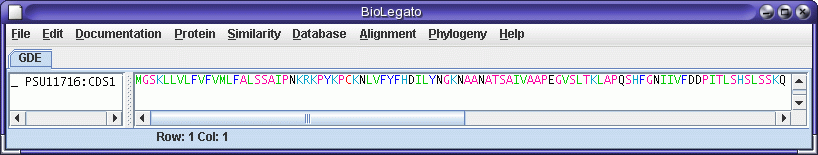
To translate into
protein, select PSU11716:CDS1, and choose DNARNA --> Ribosome. The
translated protein will be sent to a new blprotein window.
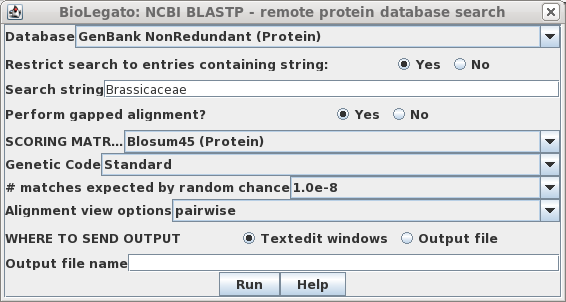
To run the BLASTP search, select the amino acid sequence and choose
Database --> NCBI BLASTP.
Choose the GenBank Nonredundant Protein
database. To limit the search to relatives of Brassica napus, click
"Yes" for Restrict search to entries containing string:, and type
"Brassicaceae" as the search string. To eliminate poor matches, set the
# matches expected by random chance to 1.0e-8 (ie. 10-8).
Click on Run to start the search.
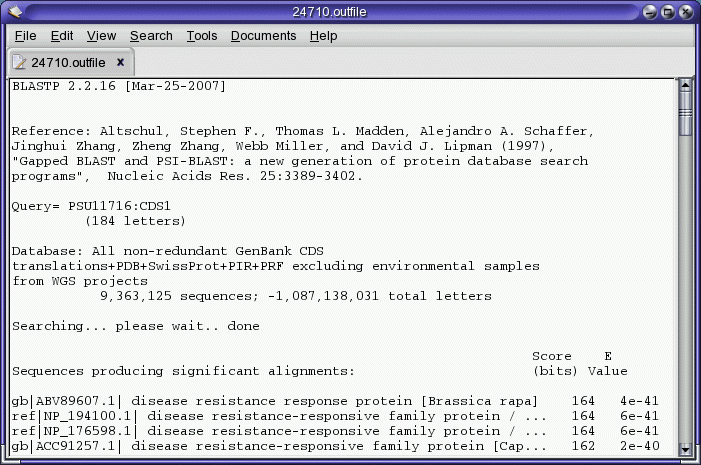
The query sequence is sent to the NCBI Blast server, and the results
are returned when complete. The results appear in several windows. The
Blast report appears in a text editor
and the Accession numbers of the hits are sent to another text editor
window:
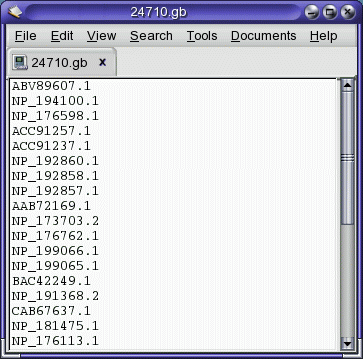
The Accession number file can be saved, and used to retrieve proteins
from the NCBI Batch Entrez service at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/batchentrez.cgi?db=Protein.






