The analysis of overrepresented sequences will spot an increase in any exactly duplicated sequences, but there are a different subset of problems where it will not work.
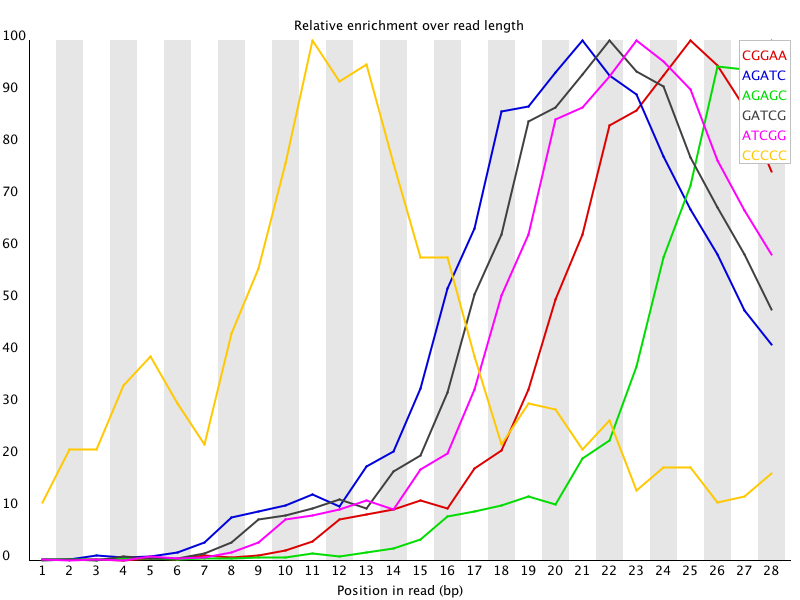
The Kmer module starts from the assumption that any small fragment of sequence should not have a positional bias in its apearance within a diverse library. There may be biological reasons why certain Kmers are enriched or depleted overall, but these biases should affect all positions within a sequence equally. This module therefore measures the number of each 7-mer at each position in your library and then uses a binomial test to look for significant deviations from an even coverage at all positions. Any Kmers with positionally biased enrichment are reported. The top 6 most biased Kmer are additionally plotted to show their distribution.

To allow this module to run in a reasonable time only 2% of the whole library is analysed and the results are extrapolated to the rest of the library. Sequences longer than 500bp are truncated to 500bp for this analysis.
This module will issue a warning if any k-mer is imbalanced with a binomial p-value <0.01.
This module will issue a warning if any k-mer is imbalanced with a binomial p-value < 10^-5.
Any individually overrepresented sequences, even if not present at a high enough threshold to trigger the overrepresented sequences module will cause the Kmers from those sequences to be highly enriched in this module. These will normally appear as sharp spikes of enrichemnt at a single point in the sequence, rather than a progressive or broad enrichment.
Libraries which derive from random priming will nearly always show Kmer bias at the start of the library due to an incomplete sampling of the possible random primers.