Per Base Sequence Content
Summary
Per Base Sequence Content plots out the proportion of each base
position in a file for which each of the four normal DNA bases
has been called.
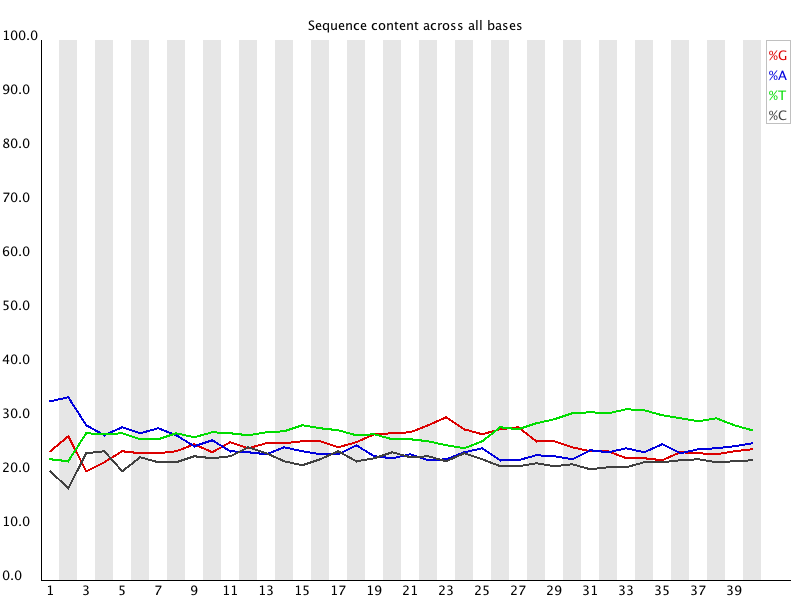
In a random library you would expect that there would be little
to no difference between the different bases of a sequence run, so
the lines in this plot should run parallel with each other. The
relative amount of each base should reflect the overall amount of
these bases in your genome, but in any case they should not be
hugely imbalanced from each other.
Warning
This module issues a warning if the difference between A and T, or G
and C is greater than 10% in any position.
Failure
This module will fail if the difference between A and T, or G and C
is greater than 20% in any position.
Common reasons for warnings
There are a number of common scenarios which would ellicit a warning
or error from this module.
- Overrepresented sequences: If there is any evidence of overrepresented
sequences such as adapter dimers or rRNA in a sample then these sequences
may bias the overall composition and their sequence will emerge from this plot.
- Biased fragmentation: Any library which is generated based on the ligation
of random hexamers or through tagmentation should theoretically have good
diversity through the sequence, but experience has shown that these libraries
always have a selection bias in around the first 12bp of each run. This is
due to a biased selection of random primers, but doesn't represent any individually
biased sequences. Nearly all RNA-Seq libraries will fail this module because of
this bias, but this is not a problem which can be fixed by processing, and it
doesn't seem to adversely affect the ablity to measure expression.
- Biased composition libraries: Some libraries are inherently biased in their
sequence composition. The most obvious example would be a library which has been
treated with sodium bisulphite which will then have converted most of the cytosines
to thymines, meaning that the base composition will be almost devoid of cytosines
and will thus trigger an error, despite this being entirely normal for that type of
library
- If you are analysing a library which has been aggressivley adapter trimmed
then you will naturally introduce a composition bias at the end of the reads as
sequences which happen to match short stretches of adapter are removed, leaving
only sequences which do not match. Sudden deviations in composition at the end
of libraries which have undergone aggressive trimming are therefore likely to be
spurious.

