Almost any gene from any species can be expressed in a plant.
BT toxin - a naturally occurring insecticidal protein from the bacterium (Bacillus thuringiensis)
Insect larvae and adults feeding on plants which express the bacterial BT toxin gene
stop feeding within 24hr. after ingestion of the toxin, and starve to
death within days of feeding.
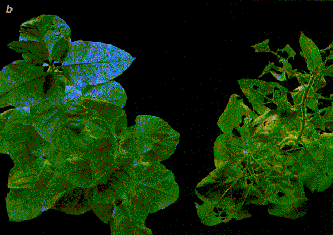
Tobacco plants expressing BT toxin (left) were largely resistant to predation by moth larvae. Untransformed tobacco plants allowed extensive feeding.
BT in potatoes

Russett Burbank potatoes were transformed with a modified BT gene encoding
a BT variant toxic to the Colorado potato beetle. The false-color image
below shows an ariel view of a field in Oregon irrigated by a center-pivot
system. In the test plots at the top of the image, green areas indicate
defoliation of quadrants planted with untransformed potatoes, and red
areas indicate transgenic test plots, which were largely untouched.
References:
Gasser CS and Fraley R (1992). Transgenic Crops. Scientific American 266:62-69. June 1992.
Perlak FJ et al. (1993) Genetically improved potatoes: protection from damage by Colorado potato beetles. Plant Molecular Biology 22:313-321.
 previous page
previous page
 next page
next page



 previous page
previous page
 next page
next page