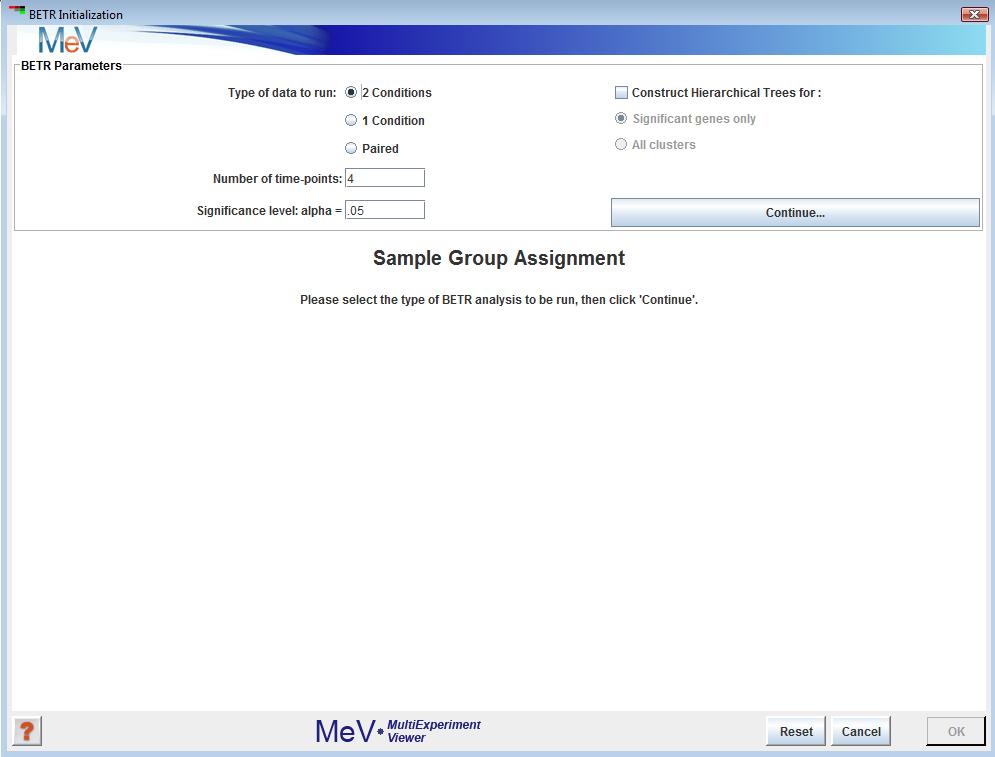
BETR Parameters
(Aryee, Martin et al , submitted 2008)
Most analyses treat time-points as independent samples and ignore potentially useful information that can be gained if the data contains non-uniform serial correlations. BETR is a flexible linear random-effects modeling framework that takes into account correlations between samples and sampling times. The method makes use of information intrinsic to the data by modeling the joint distribution across all samples. Each gene is given a probability of differential expression that is derived from an empirical Bayes approach that uses the whole data set to reduce the number of parameters to be estimated.
The BETR method can be applied to one-color or two-color microarray data. The user may also select one-condition which will find differences between a baseline, t = 0, in a single condition.
After opening the BETR initialization dialog, select the type of data you intend to run. Your 3 options are:
Input the number of time-points that your data contains. If you are running 1-Condition data, the control is treated as the first time-point.
Assign a significance level
Genes assigned a significance greater than 1-alpha will be deemed significant. Click “Continue” to move to the next step.
Assign your samples
Depending on the type of data you have selected, you will need to assign your samples to time-points and conditions, if necessary.
Button Selection
Use this option if you have not created clusters for your samples and want to assign each sample individually.
Each time-point must contain at least two samples assigned to it.
For 2-Condition data, both conditions must have at least two samples assigned to each of its genes.
If you have failed to adequately assign samples a dialog will pop up helping you find the condition and/or time-point that has insufficient samples.
Cluster Selection
Use the cluster selection panel if you have previously made clusters and wish to run your analysis based on those clusters. Use the drop-down boxes to choose which clusters’ samples are to be assigned to which time-points. For clusters you are not using, leave “unassigned”. The same condition and time-point requirements exist for this method, but the cluster selector makes for easier and more organized sample assignment.
Hierarchical Clustering
To have BETR construct hierarchical trees for your results, check the corresponding check box. Select whether this feature is to be applied to significant genes or significant and non-significant genes. This process may add significantly to the computation time.
The BETR module outputs standard viewers and tables for MeV’s statistics analyses.