Key Types of Bonding in Chemistry

Course Menu
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are a chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositley charged ions. The atoms acutually physically loose or gain electrons and for either positively or negatively charged ions. This is demonstrated below:
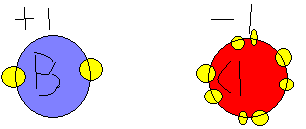
Where B is Boron and Cl is Clorine. The Boron atom gets rid of one of it's electrons since it had 1 electron in it's outer valence. It is now in it's most stable state with a full valence. Since Boron has lost 1 electron it becomes positively charged because there are now more protons than electrons: hence +1 charge. Clorine accepted the lone electron to fill it's outter valence and now it has satisfied it's valence and it is now full. Clorine now has 1 more electron than it has protons. This is why it now has a -1 charge. These 2 atoms now are called ions because of their charges.
- Cations
- are the atom that gives away their electron
- obtains a positive charge because there are now more protons than electrons
- Anions
- are the atom that accepts the electron
- obtains a negative charge because there are now more electrons than protons
If you have further questions and would like to discuss the problems that you are having feel free to contact me at:
Melanie Lalonde123 Fun Street
Winnipeg,MB, T3C4C6
or if it is more convient you can always e-mail!
*copyright 2009 by Melanie Lalonde* *Internet Explorer V 8*